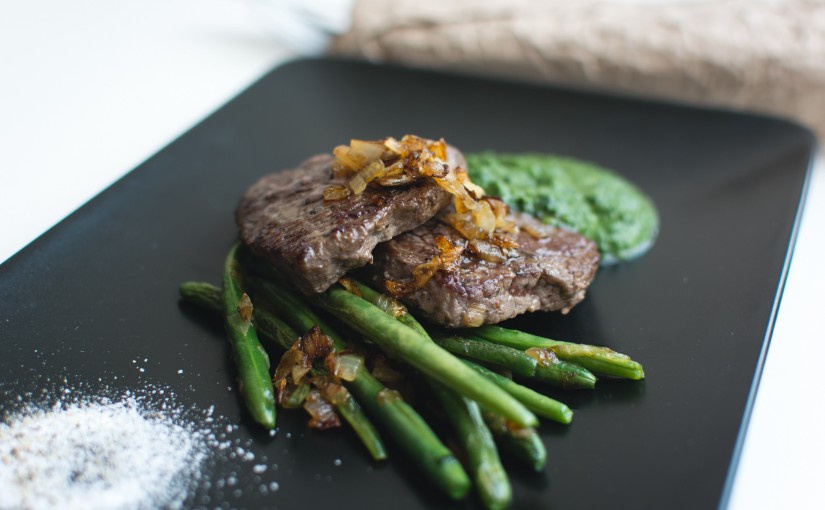
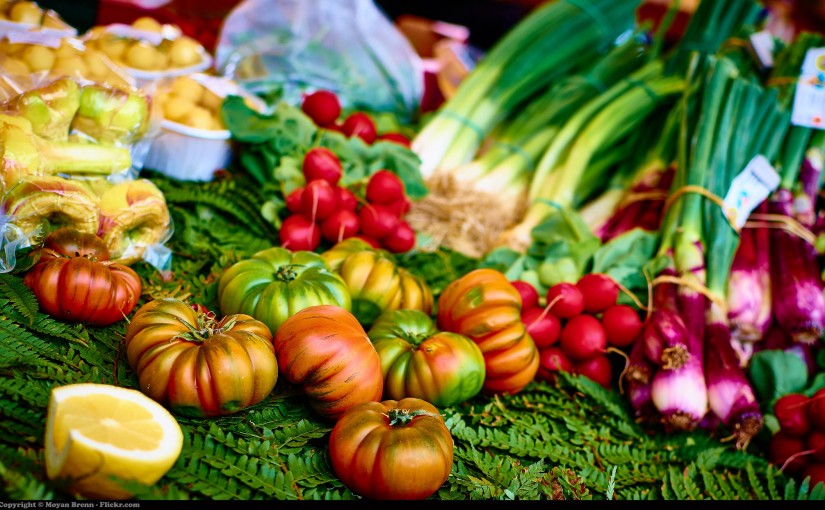
As far as diets go, paleo is both very new and very old. At first, this may seem like a contradiction, but people have been eating in this fashion for millions of years, ever since the first hunter-gatherer tribes appeared on Earth. However, it was only just recently that we became aware of the health benefits of this historical way of eating. Whether you are planning on embracing the paleo lifestyle or just curious about the health benefits of this type of diet, then this article is for you. Here we will outline the health benefits of paleo so that you can decide whether it is for you. Paleo, for this article’s purposes, is the act of eating as our hunter-gatherer ancestors did. This means that you are allowed to eat foods which could be gathered from the ground or pulled from trees as are free-range, grass-fed animals. Gluten is prohibited, as are all processed foods as much as possible. This more natural way of eating of course promotes a number of health benefits.
Real Food Vs. Processed Food
Processed foods contain a lot of additives, preservatives, colorings, sodium and hidden sugar. These chemicals are not good for our bodies, causing everything from allergic reactions to sluggishness to high blood pressure. If you eat a paleo diet, which contains only whole, organically produced foods and some natural but packaged sauces and ingredients, you eliminate a large number of toxins from your body as well as the salt which raises your blood pressure and the hidden sugar that can increase your risk of diabetes and becoming overweight. Eliminating additives, preservatives and other unnecessary chemicals from your food also helps you feel much better, both mentally and physically, helping your body work at peak performance.
Get Your Nutrients
Along with the benefit of removing preservatives, the paleo diet also removes nutrient-void carbs. People eating in this manner tend to replace the filler carbs with fruits, vegetables and healthy fats. In fact, a person eating a paleo diet can get all the required nutrients for a day from plant-based foods, meat and fish. They eliminate grains and legumes, which also leads to increased gut health. Increased gut health, in turn means that their bodies digest food much more efficiently.
Weight Loss
Paleo diets promote a long-lasting weight loss and muscle growth when paired with a healthy lifestyle. Better stress management techniques as well as an improvement in sleep and a good balance of Omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids help to burn off stored fat. Also, eating a paleo diet will increase your energy, which will allow you to exercise longer without tiring.
Lose the Bloat
Many people eating a Western-style diet find themselves experiencing chronic bloat and gas which can be very uncomfortable. Eating a paleo diet reduces these symptoms, as paleo diets contain a lot of fiber. Fiber allows waste products in the body to be broken up more effectively and carried away, thereby eliminating constipation which can lead to much worse issues such as compaction. Those on paleo diets also drink an adequate amount of water and decrease their sodium intake. This both flushes out the waste and prevents water retention, which can lead to bloat.
Avoid Blood Sugar Crashes
If you have ever been in an important meeting at work and have suddenly found your mood plummeting as you got hungrier, then you have experienced a blood sugar crash. Eating a paleo diet can be very helpful in preventing these crashes and the accompanying spikes that occur when we eat because they are very rich in protein, fats, and slow-digesting carbs. Meals with a lot of protein and fat are very energy-dense and satisfying. This means you feel full sooner than if you were eating something like a bag of chips that was unbalanced. Carbs all raise your blood sugar a bit, but slow-digesting carbs do not raise it nearly as much. Nor do they let it drop as quickly. Slow-digesting carbs take a long time to be metabolized. This means that you will become hungry more slowly and without the irritabality and mood swings you might normally experience.
There are many benefits to a paleo diet. These are only a few. Paleo diets are rich in healthy fats, proteins, fruits, vegetables and slow-digesting carbs. This makes them the exact balance of the foods your body needs and people have been eating this way for millennia and still do in other parts of the world. These people are living happy, healthy lives, free from most of the health problems that face the Western world. Would it not be nice to live a life in which you had less of a risk of most of those problems? If you agree, then paleo just might be the right lifestyle choice for you.